4 Attachment Styles in Relationships

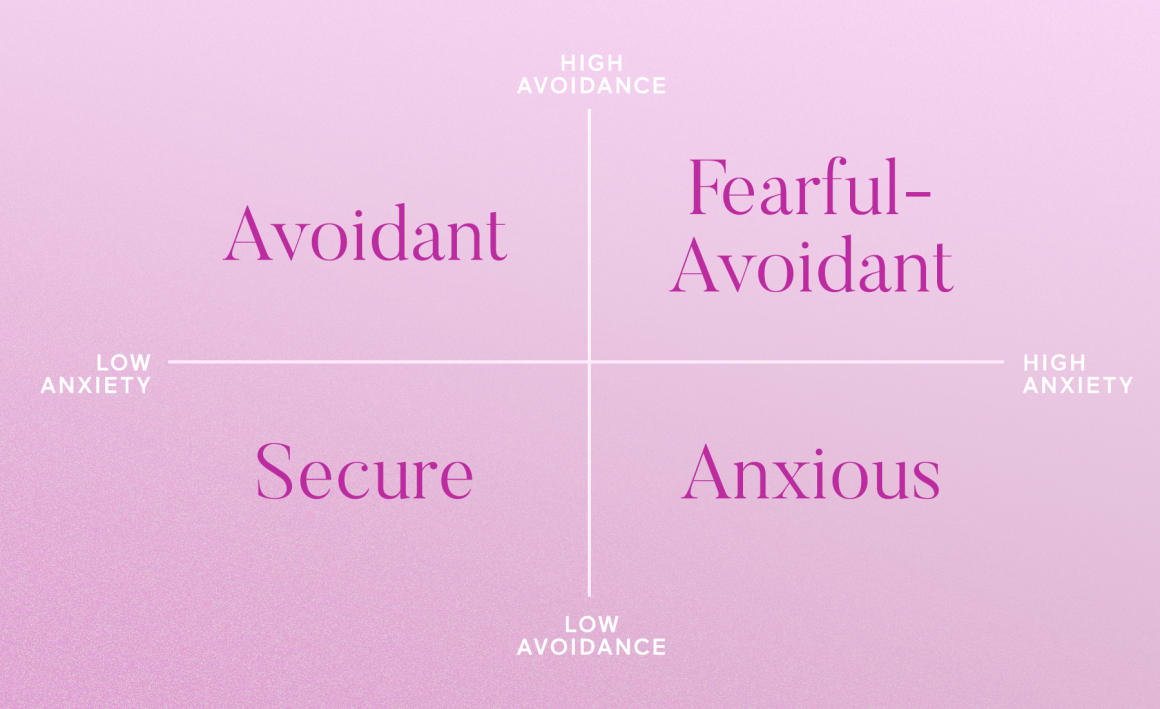
Listed below are 4 Attachment Styles in Relationships. Each of them has their own unique characteristics and traits. Understanding the different styles will help you improve your relationships. These styles include Avoidant, Anxious-Preoccupied, Dismissive-Avoidant, and Ambivalent.
Avoidant attachment style
Avoidant attachment is a style of attachment that is difficult to understand but can make relationships more fulfilling and secure. This style of attachment is learned through experiences of emotional neglect and insensitivity in the early years of life. As a result, people who are avoidant often avoid intimacy and try to hide their feelings when confronted with emotional situations.
People with this style of attachment fear connection and may bail out of a relationship if it reaches a certain point. Developing a connection with someone with this style is difficult because it can feel like you’re running into a brick wall. However, love is possible, even for avoidantly attached people. You just need to be patient.
The first step in healing is admitting you have an avoidant attachment style. You’ve probably tried to avoid acknowledging the negative effects of your childhood and your own behavior. But this will only help you become aware of your own triggers. A common trigger is a lack of affection or lack of intimacy. In addition, avoidants tend to associate vulnerability with rejection or shame.

The opposite of loving and being loved, the avoidant style of attachment can cause a partner to distrust physical touch. They don’t want to hurt anyone and therefore are afraid to share their feelings. When this happens, they may turn to gift giving to mask their fear of intimacy. When this happens, they may end up accusing their partner of being overprotective or clingy.
Anxious-preoccupied style
Those with the Anxious-Preoccupied style of attachment in relationships are highly emotional and often have difficulty communicating their feelings. Because they have a strong need to protect themselves from abandonment Styles in Relationships, they are alert to changes in their partners’ emotional expression. These people also have a tendency to make snap judgments and misinterpret other people’s emotional states. In order to deal with anxiety, they must learn to communicate their feelings more clearly and build strong bonds with their partners.
People with Anxious-Preoccupied style of attachment often have a troubled past. They may have been neglected or abused as children. As a result, they experience a fear that they will never be loved. This fear often makes them feel insecure in relationships.
Dismissive-Avoidant style
A Dismissive-Avoidant partner will be distant from you and put you low on his or her priority list. When you ask for assurance from him or her, they will not respond, letting you know that the relationship is not important. Their lack of emotional expression is often accompanied by physical symptoms.
The Dismissive-Avoidant style of relationship attachment is often a result of early childhood experiences. This style has been associated with a high self-image and an avoidance of intimacy. They have a hard time expressing their feelings and find it difficult to ask for help. This type of person is likely to criticize other people and not be able to accept their partners’ needs.
While avoidant-dismissive attachment can affect older adults, the same patterns are present in younger children as well. Unlike the avoidant-dismissive attachment style in adults, children who display this pattern can still be protected by their parents. Parents can encourage their children to express their emotions and let them know they are cared for and safe.
Ambivalent attachment style
Couples with ambivalent attachment styles may find it difficult to express their true feelings. When a partner does not express their feelings, it can be triggering for them. To combat this, you need to make sure that you are consistently showing your love for your partner. Otherwise, you risk reinforcing their fears. When a partner experiences inconsistent affection, it mirrors the developmental stages of their early years and exacerbates their anxiety.
People with this attachment style usually lack personal autonomy and require constant recognition and attention. They may suffer more in a relationship if it has a rigid structure. Because of these issues, they often ask for more emotional connection. They are also prone to breakups. It is crucial that both partners know the type of attachment style that they have, and choose partners accordingly. Regardless of their aversion to commitment, this type of person needs a partner who can make them feel secure.
Identifying your partner’s attachment style is important if you want to avoid conflict in your relationship. Whether your partner has a secure or an insecure attachment style, it is essential to understand how each style affects your partner.



